2025 How to Choose the Right Wire Cable for Your Projects Effectively
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology and construction, the importance of selecting the right wire cable for any project cannot be overstated. Experts in the field emphasize that the choice of wire cable significantly impacts not only the efficiency of the project but also its overall safety and longevity. John Stevens, a veteran electrical engineer and wire cable specialist, once stated, "Choosing the right wire cable is crucial; it is the backbone of any electrical system, ensuring reliability and performance."
As projects grow in complexity, so too do the options available in the wire cable market. With myriad types, sizes, and specifications, making an informed choice can be daunting. Understanding the fundamental characteristics of wire cables—such as gauge, insulation type, and material—can make all the difference when aiming for optimal functionality. Therefore, it is essential for project managers and engineers alike to consider these factors meticulously.
Striking the right balance between performance requirements and budget constraints calls for not just knowledge but also a strategic approach. This means evaluating the specific needs of each project, along with potential challenges, while staying abreast of industry standards and advancements. With this comprehensive outlook, individuals can confidently navigate the wire cable selection process, ultimately enhancing the quality and safety of their projects.

Understanding Wire Cable Types: An Overview of Common Standards
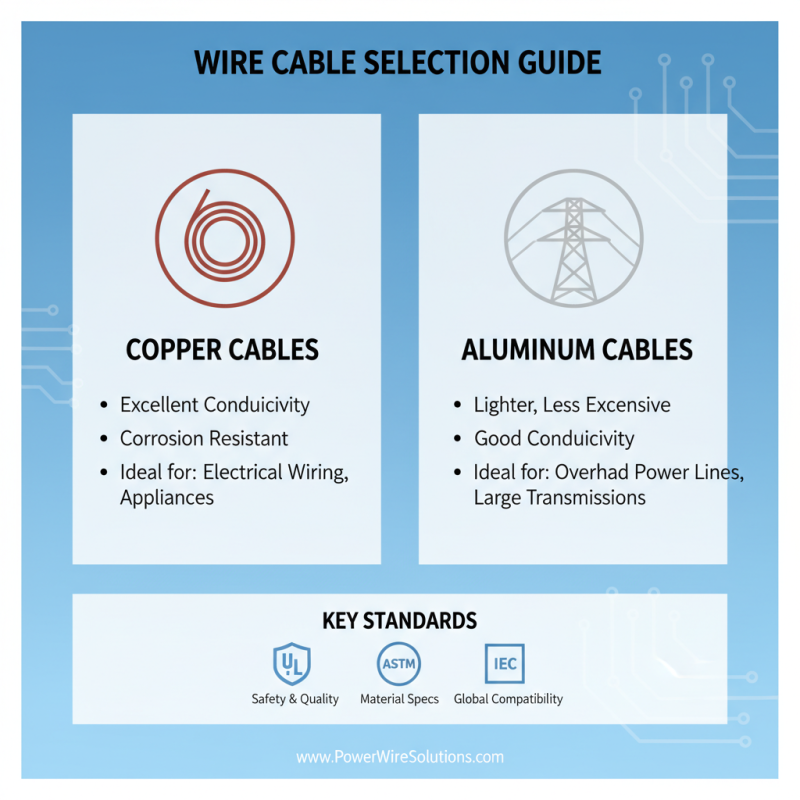
When selecting the right wire cable for various projects, understanding the different types and their standards is crucial. Wire cables come in a multitude of forms, each designed for specific applications. For instance, copper and aluminum are the most common conductive materials used in wire cables. Copper offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical installations, while aluminum is lighter and less expensive, often used in overhead power lines.
In addition to material differences, wire cables are categorized according to various standards, such as AWG (American Wire Gauge), which indicates the thickness of the wire. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) can carry more current and are often used in high-demand conditions. Other standards include the NEC (National Electrical Code) that governs the installation of electrical wiring, ensuring safety and functionality. Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the right wire cable that not only meets the technical requirements of a project but also adheres to safety guidelines.
Key Considerations for Voltage Ratings: Ensuring Safety and Performance
When selecting wire cables for your projects, understanding voltage ratings is imperative for ensuring both safety and optimal performance. Voltage ratings determine the maximum voltage a wire can handle without experiencing electrical breakdown or damage. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), wires are often categorized by their insulation types, which directly influence their voltage ratings. For instance, commonly used types like THHN or THWN are rated for 600 volts, while certain specialty wires can handle significantly higher voltages. Recognizing these classifications can prevent accidents and ensure your project complies with relevant safety standards.
Tips: Always check the insulation type of the wire you choose. For high-voltage applications, selecting wires with appropriate insulation characteristics, such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or Thermoset materials, can provide better performance and longevity.
Furthermore, the environment in which the wire will be used can also affect the selection of voltage ratings. For instance, cables exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures may require wires with specific ratings and materials designed to withstand such conditions. A report from the International Electrotechnical Commission suggests that environmental factors can decrease the effective lifespan of cables by up to 50% if improper ratings are used.
Tips: Conduct a thorough assessment of your project environment to choose a wire cable that not only meets voltage requirements but also has the durability needed for its surroundings.
The Role of Material Composition: Copper vs. Aluminum in Cable Selection
When selecting wire cables for various projects, understanding the material composition is crucial, particularly when comparing copper and aluminum. Copper cables are renowned for their excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of approximately 59 MS/m. This characteristic makes copper the preferred choice for applications requiring high performance, such as in telecommunications and power generation. According to a report by the International Copper Association, copper cables also exhibit superior thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, which can lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer service life.
On the other hand, aluminum cables present a compelling alternative due to their lightweight nature and lower cost. While aluminum has a conductivity rating of around 37 MS/m, which is lower than that of copper, advancements in alloy technology have allowed for the development of aluminum cables that can match or exceed the performance of traditional copper cables in specific applications. The Aluminum Association suggests that aluminum can be a suitable choice for overhead power lines and large-scale electrical distribution systems, where weight considerations outweigh conductivity. Ultimately, choosing the right cable material depends on the specific requirements of the project, including environmental factors, load capacity, and budget constraints, making a thorough assessment of both copper and aluminum options essential.
2025 How to Choose the Right Wire Cable for Your Projects Effectively - The Role of Material Composition: Copper vs. Aluminum in Cable Selection
| Attribute | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High (Conductivity: ~ 59.6 MS/m) | Moderate (Conductivity: ~ 37.7 MS/m) |
| Weight | Heavier (Approx. 8.96 g/cm³) | Lighter (Approx. 2.70 g/cm³) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Fair (Can oxidize) |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Applications | Electrical wiring, electronics | Power transmission, overhead lines |
Evaluating Cable Insulation: Temperature and Environment Compatibility
When selecting wire cables for various projects, a crucial aspect to consider is the insulation material, particularly its compatibility with temperature and environmental conditions. Different applications can expose cables to a wide range of temperatures, from extreme cold to intense heat. Insulation materials, such as PVC, Teflon, or rubber, each have distinct temperature tolerances. Understanding these limits is vital to ensure the cable will perform reliably throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Moreover, the installation environment plays a significant role in determining the type of insulation needed. Factors such as exposure to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation can degrade cables over time. For instance, in industrial settings or outdoor installations, choosing cables with UV-resistant and waterproof insulation is essential to prevent premature failure. Evaluating these environmental factors can save time and resources by avoiding frequent replacements and ensuring the integrity of electrical connections in the long run. Careful consideration of both temperature and environmental compatibility will guide you in selecting the most effective wire cables for your projects.
Evaluating Cable Insulation: Temperature and Environment Compatibility
Industry Best Practices: Sizing Wire Cables for Load and Application Efficiency
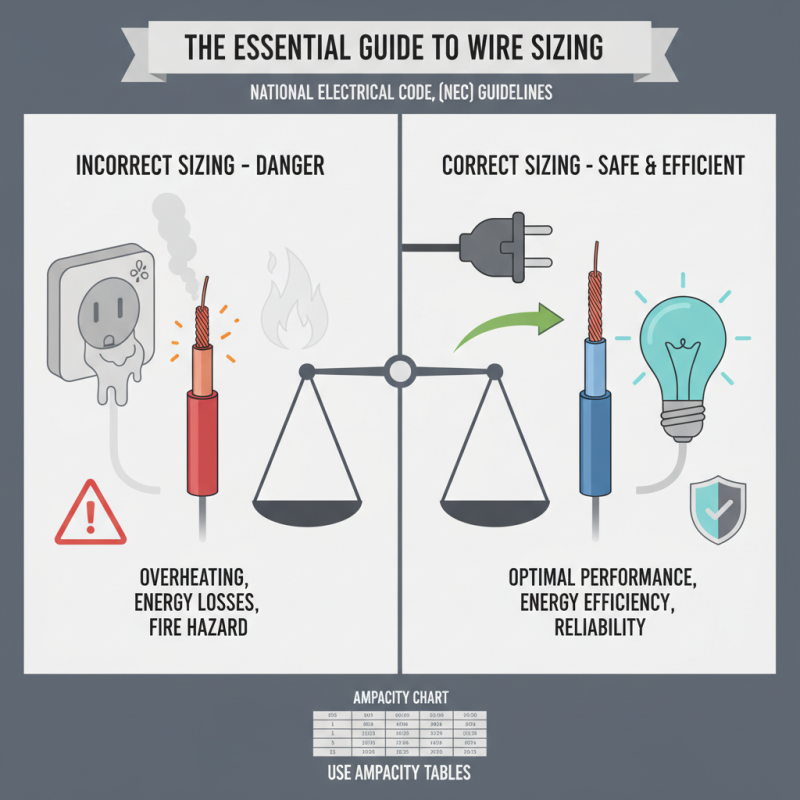
When selecting the appropriate wire cable for any project, understanding the load requirements and application efficiencies is critical. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), improper sizing can lead to inadequate performance, increased energy losses, and potential safety hazards. For instance, a wire that is too small may overheat due to excessive current flow, which not only damages the wire but can also pose fire risks. The NEC recommends utilizing the ampacity tables to determine the ideal wire gauge based on the expected current load and installation environment.
Additionally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) suggests that environmental factors such as temperature, insulation type, and installation method must be considered when sizing wire cables. In a report published by the IEC, it was noted that overlooking these factors can decrease the operational efficiency of electrical systems by up to 30%. For example, conducting installations in high-temperature environments can drastically lower the wire's current-carrying capacity, necessitating the use of larger wire sizes to maintain functionality and safety. Hence, adhering to these industry best practices is essential for ensuring that wiring solutions are not just compliant but also optimized for peak performance and longevity.
Related Posts
-

Mastering Cord Management for a Clutter Free Home Environment
-

Exploring HDMI Switcher Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-
Emerging Trends in HDMI Fiber Optic Cable Market at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Understanding HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Revolutionizing Home Entertainment Systems
-

Exploring the Future of Coax Cable Innovations at China’s 138th Import and Export Fair 2025
-

What is RCA Jacks Understanding Their Types and Uses in Audio Systems
