Top 10 RF Cable Types and Their Uses for Enhanced Signal Transmission
In the rapidly evolving world of telecommunications, the importance of optimizing signal transmission cannot be overstated. RF cables play a crucial role in facilitating the efficient transfer of radio frequency signals across various applications, from consumer electronics to critical infrastructure. Renowned RF industry expert Dr. Emily Rodriguez stated, "The choice of RF cable can significantly impact the performance of your system, making it imperative to understand the different types and their specific uses."
As we navigate through the top 10 RF cable types, it's essential to recognize how each type caters to distinct requirements and environments. From low-loss cables designed for long-distance transmission to flexible options suitable for intricate setups, the landscape of RF cabling provides a plethora of solutions tailored to enhance signal quality. In the following sections, we will delve into the characteristics, applications, and advantages of various RF cable types, equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions for their specific needs. Understanding these nuances will not only optimize performance but also ensure reliability in every communication system that relies on these vital components.
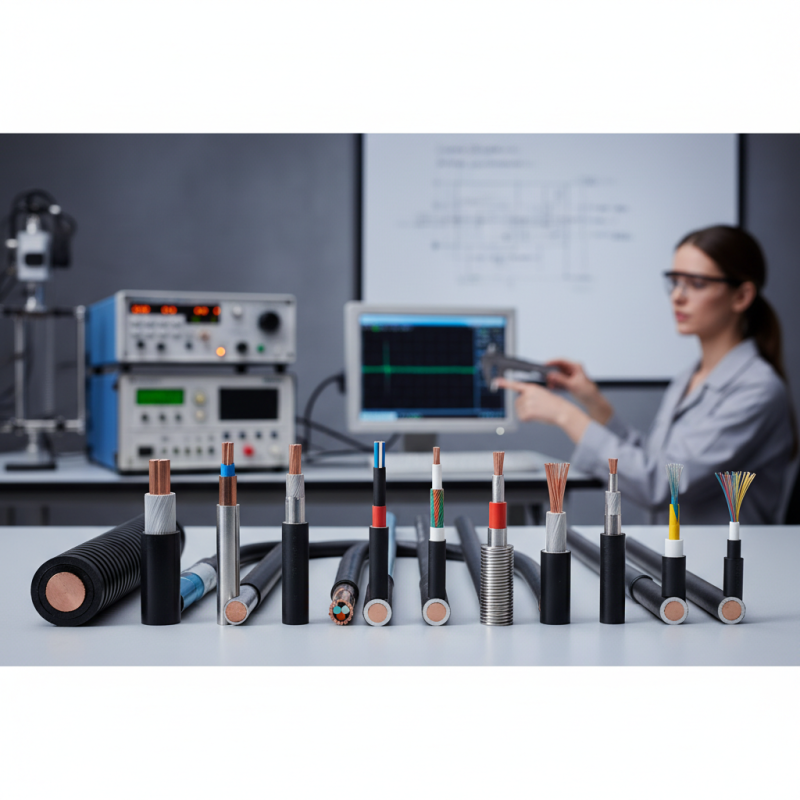

Types of RF Cables: An Overview of Signal Transmission Solutions

When it comes to enhancing signal transmission, understanding the various types of RF cables is essential. RF cables play a crucial role in transferring radio frequency signals from one point to another, making them fundamental in applications such as telecommunications, broadcasting, and satellite communications. The design of these cables often dictates their functionality, durability, and efficiency in signal transmission. Common types include coaxial cables, which are known for their versatility and minimal interference; twisted pair cables, which provide good performance in data communications; and fiber optic cables, which are indispensable for high-speed data transfer over long distances.
In addition to these, there are specialized cables designed for specific use cases. For instance, semi-rigid cables are favored in environments where space is limited and precision is critical, while flexible cables cater to dynamic applications that require bending and movement. Understanding the distinct characteristics of each cable type allows professionals to select the most suitable solution for their signal transmission needs, ensuring optimal performance. Whether enhancing television reception, facilitating wireless communication, or supporting data transfer, the right RF cable can significantly improve overall system efficiency.
Coaxial Cables: The Workhorse of RF Signal Distribution
Coaxial cables have long been recognized as the essential backbone of RF signal distribution. These cables, characterized by their unique construction of a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator, metallic shield, and outer insulating layer, provide significant advantages in minimizing signal loss and electromagnetic interference. According to a 2022 industry report, coaxial cables can achieve a frequency range of up to 18 GHz, making them suitable for a variety of applications, from television broadcasting to network infrastructure.
When selecting coaxial cables for RF applications, it’s crucial to consider factors such as attenuation and impedance. The most common impedance levels are 50 and 75 ohms, each tailored for specific applications; 50-ohm cables are ideal for RF transmission, while 75-ohm cables are typically used for video signal transmission. Additionally, a study by the Telecommunications Industry Association highlights that using high-quality coaxial cables can reduce signal degradation by as much as 30%, ensuring reliable performance for critical communications.
Tips: When installing coaxial cables, ensure that the connectors are properly attached to avoid loss of signal quality. Using appropriate cable management techniques can also prevent unwanted bends and kinks, which compromise the cable's effectiveness. Regularly inspect cables for wear and tear to maintain optimal performance.
Ribbon Cables: Flexibility and Space-Saving Designs in RF Applications

Ribbon cables have emerged as a preferred choice in RF applications due to their unique design which offers both flexibility and a compact footprint. Unlike traditional coaxial cables, ribbon cables consist of multiple conductors arranged in a flat, parallel configuration. This structure reduces the electromagnetic interference (EMI) and maintains consistent impedance across channels, which is essential for enhanced signal transmission. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the use of ribbon cables in RF systems can improve signal integrity by as much as 30% compared to conventional wiring solutions.
The flexibility of ribbon cables is particularly advantageous in space-constrained environments such as data centers and telecommunications equipment where efficient cable management is crucial. By employing flat ribbon cables, engineers can reduce clutter and allow for easier routing around obstacles. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Network and Systems Management highlighted that implementing ribbon cabling reduced installation time by nearly 25%, demonstrating significant labor cost savings. This flexibility, combined with their ability to maintain signal quality over longer distances, solidifies ribbon cables as an essential component in modern RF applications where performance and space efficiency are paramount.
Fiber Optic Cables: High-Speed Data Transfer for RF Technologies
Fiber optic cables are emerging as a critical component in enhancing RF technologies, particularly for high-speed data transfer. According to a report from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), fiber optic technology can facilitate data transmission speeds exceeding 100 Gbps, significantly outpacing traditional copper RF cables. This advancement is especially crucial in applications requiring large bandwidths, such as 5G networks and data centers, where the demand for rapid and reliable data transfer continues to grow.
The adoption of fiber optic cables in RF applications is further supported by industry projections indicating a substantial increase in global fiber optic cable usage. A report by MarketsandMarkets anticipates that the fiber optics market will reach USD 6.9 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.2%. This trend highlights the significant shift towards optical solutions, driven by the need for improved performance in data transmission, reduced latency, and enhanced signal integrity. As RF technologies evolve, the integration of fiber optics is set to play a vital role in meeting the increasing demands for higher data rates and more robust communication infrastructures.
Choosing the Right RF Cable: Factors Influencing Signal Quality
When selecting the right RF cable, several factors significantly influence signal quality and overall performance. First and foremost, the cable's impedance must match the system it is designed for, typically either 50 or 75 ohms. A mismatch can lead to signal reflections and losses, compromising the integrity of the transmission. Additionally, the cable length plays a crucial role; longer cables can introduce more attenuation, which diminishes the signal strength as it travels through the medium. Therefore, careful consideration of the required distance and the environment where the cable will be used is essential for optimal performance.
Furthermore, cable construction and material are key to ensuring high-quality signal transmission. The choice of conductor, insulator, and shielding material influences the cable's ability to resist interference and maintain low loss. For example, cables with high-quality copper conductors usually offer better conductivity than those made with cheaper materials. Additionally, cable shielding, whether foil or braided, can protect against external electromagnetic interference, which is vital in scenarios where signals can be affected by nearby electronic devices. Understanding these elements will enable users to select RF cables that maximize signal quality and enhance overall communication effectiveness.
Top 10 RF Cable Types and Their Uses for Enhanced Signal Transmission
| Cable Type | Frequency Range | Impedance | Typical Use | Signal Loss (dB/100ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG-6 | 5 MHz - 1 GHz | 75 Ohm | Cable TV, Satellite | 3.5 |
| RG-58 | 0 - 1 GHz | 50 Ohm | Radio Frequency, Wi-Fi | 6.2 |
| RG-11 | 5 MHz - 1 GHz | 75 Ohm | Satellite, Cable Internet | 2.8 |
| RG-213 | 0 - 2 GHz | 50 Ohm | Communication Systems | 4.2 |
| LMR-400 | 0 - 6 GHz | 50 Ohm | Wireless Communication | 2.5 |
| RG-8 | 0 - 1 GHz | 50 Ohm | Amateur Radio | 6.4 |
| CTC-400 | 0 - 6 GHz | 50 Ohm | Broadcast Transmission | 2.7 |
| RG-174 | 0 - 3 GHz | 50 Ohm | GPS, Cellular | 10.0 |
| SMA Cable | 0 - 18 GHz | 50 Ohm | Precision RF Applications | 1.3 |
| HDF-400 | 0 - 6 GHz | 50 Ohm | High Definition Video Transmission | 2.1 |
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Phone Cable for Your Devices
-

2025 How to Choose the Right HDMI Connectors for Your Devices
-

2025 Top 10 Best Telephone Wire for Quality and Durability
-

2025 Top 5 Fiber Network Cable Innovations for High Speed Connectivity
-
Harnessing Fiber Optic Adapter Innovations at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Why You Should Choose Fiber Optic Patch Cable for Reliable High Speed Internet Connection
