The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Wire Cable Types for Your Projects
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the importance of selecting the right wire cable for various projects cannot be overstated. According to a recent report by Research and Markets, the global wire and cable market is expected to reach $228.83 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This growth underscores the critical role that wire cable plays in sectors such as construction, telecommunications, and automotive industries. Understanding the different types of wire cable—ranging from low-voltage options to high-capacity power cables—enables professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike to make informed decisions that enhance safety and efficiency. In this guide, we will delve into the various wire cable types, their applications, and best practices to help you select the most suitable option for your projects.
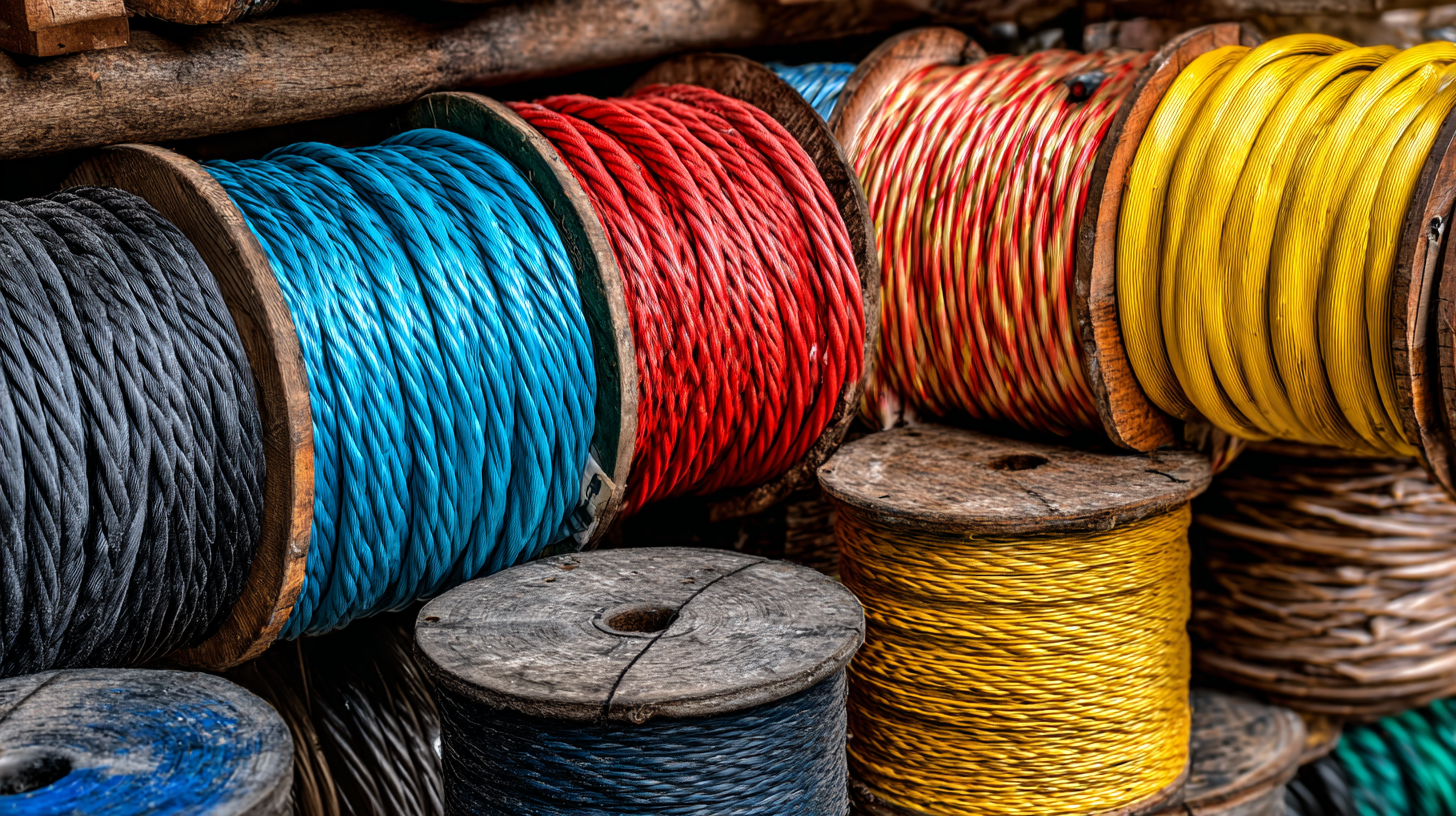

Types of Wire Cables: A Comprehensive Overview for Beginners
When embarking on a project that requires wiring, understanding the various types of wire cables is essential for achieving optimal results. For beginners, it can be overwhelming to navigate the myriad options available. Wire cables can be broadly categorized into several types: copper, aluminum, coaxial, fiber optic, and more. Each type serves a specific purpose, making it crucial to select the right cable for your needs.
Copper wire cables, known for their excellent conductivity and durability, are often used in electrical applications. Aluminum cables are lighter and more cost-effective, making them popular for overhead power lines. On the other hand, coaxial cables are primarily utilized for transmitting radio frequency signals, particularly in television and internet connections. Meanwhile, fiber optic cables utilize light to transmit data, offering high speeds and minimal loss over long distances, making them ideal for networking applications. Understanding these key differences will empower you to make informed decisions when selecting wire cables for your projects.
Understanding the Specifications: Gauge, Insulation, and Strength
Choosing the right wire cable for your projects involves understanding key specifications such as gauge, insulation, and strength.
Wire gauge, measured in AWG (American Wire Gauge), is critical as it determines the current-carrying capacity and resistance of the wire. For example, a
14 AWG wire can handle up to 15 amps safely, while a
10 AWG wire can manage up to 30 amps. According to the
National Electrical Code (NEC), using a wire gauge that is too small for your application's needs can lead to
overheating and potential fire hazards.
Insulation type is another essential factor, impacting both safety and performance. Common insulation materials,
such as PVC and XLPE, are rated for different temperature ranges and environmental conditions. Data from the
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) indicates that cables with thermoplastic insulation can
withstand temperatures up to 75°C, while thermosetting varieties like XLPE can endure temperatures
as high as 90°C. Finally, strength metrics, including
tensile strength and pull-out force, must be considered, especially in applications where the wire will
experience mechanical stress. According to the
American Wire Gauge Standards, understanding these specifications ensures that your electrical systems
function reliably and safely.
Choosing the Right Wire Cable for Your Project Needs
When embarking on any electrical project, selecting the appropriate wire cable is crucial to ensure efficiency and safety. The NEMA emphasizes that using the correct wire type can significantly reduce energy loss and enhance the overall performance of electrical systems. For residential installations, copper wiring is often preferred due to its lower resistance and excellent conductivity compared to aluminum. In fact, the U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that homes using copper wiring can save up to 10% on energy bills annually due to improved electrical flow.
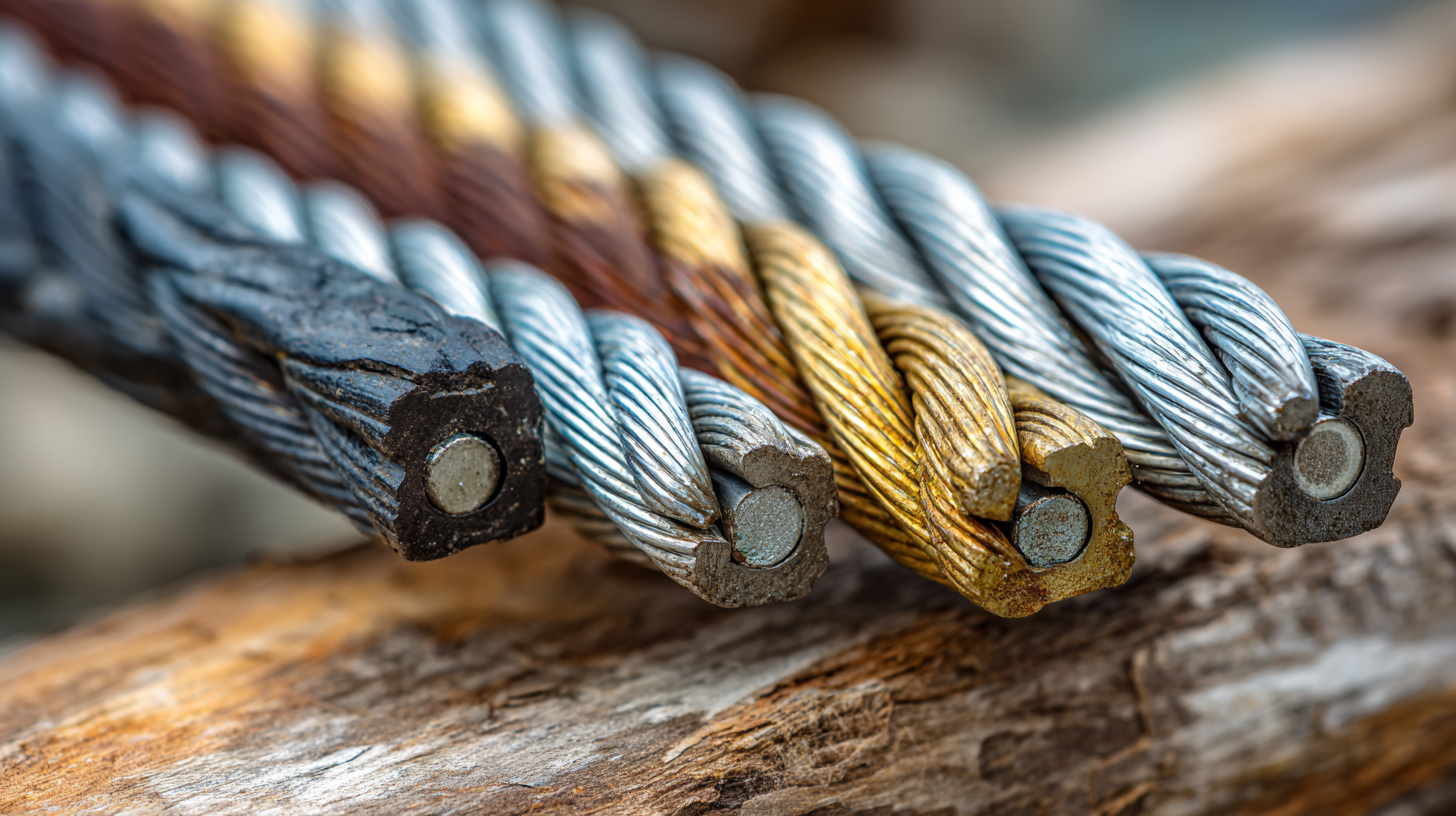

Moreover, environmental factors must be considered when choosing wire cables. For outdoor applications, cables need to be rated for moisture resistance and UV protection. According to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), improperly insulated cables can lead to failures in electrical systems, which can result in costly repairs and safety hazards. By understanding the specific requirements of your project and consulting industry standards, such as those published by the American Wire Gauge (AWG), you can make informed decisions that meet both regulatory compliance and performance specifications, ultimately ensuring the longevity and safety of your installations.
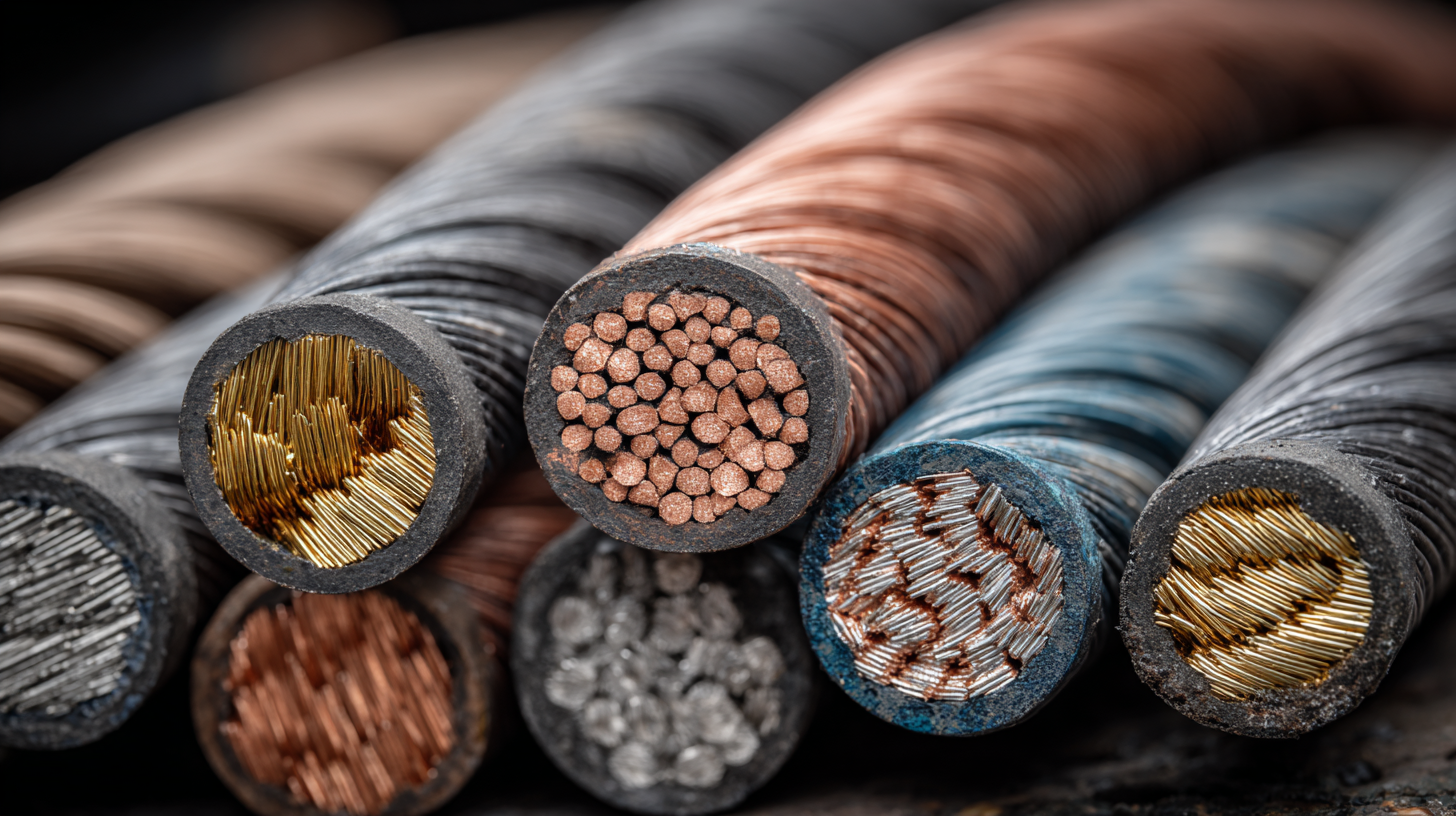
Common Applications of Different Wire Cable Types Explained
When undertaking any project involving electrical work, it’s essential to understand the different wire cable types and their common applications. Each type of wire cable is designed to handle specific tasks, ensuring safety and efficiency. For instance, THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated) wire is particularly popular in residential and commercial construction due to its versatility and heat resistance. It is commonly used for wiring in walls, conduits, and for various indoor applications.
Another important type is the UF (Underground Feeder) cable, which is designed for outdoor use and can be buried directly in the ground. This makes it ideal for powering outdoor lighting, garden equipment, and other landscape features without the need for conduit. Additionally, the use of coaxial cable is prevalent in communication projects, such as transmitting cable television signals and broadband internet. Its construction helps minimize signal loss over distances, making it a reliable choice for both residential and commercial installations. Understanding these applications will enable you to select the right wire cable type for your specific needs, ensuring both functionality and compliance with safety standards.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Using Wire Cables Effectively
 When working with wire cables, ensuring proper maintenance is essential for
safety and performance. Regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs
of wear, fraying, or corrosion. Check the connections and terminations to ensure they are secure and free from
damage. If you notice any abnormalities, replace the affected cables immediately to
prevent potential failures during operation.
When working with wire cables, ensuring proper maintenance is essential for
safety and performance. Regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs
of wear, fraying, or corrosion. Check the connections and terminations to ensure they are secure and free from
damage. If you notice any abnormalities, replace the affected cables immediately to
prevent potential failures during operation.
Additionally, proper handling and storage of wire cables can significantly extend their lifespan. Avoid unnecessary
bending or twisting, and store cables in a dry, cool environment to
prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to corrosion. Use cable organizers to prevent tangling, and always adhere to
the manufacturer's guidelines regarding load capacity and usage to ensure safe operations. By implementing these
maintenance and safety tips, you can effectively utilize wire cables in your
projects while minimizing risks.
Related Posts
-

Exploring HDMI Switcher Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-
Emerging Trends in HDMI Fiber Optic Cable Market at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Exploring the Future of Coax Cable Innovations at China’s 138th Import and Export Fair 2025
-
Harnessing Fiber Optic Adapter Innovations at China Import and Export Fair 2025
