Understanding Wire Cable Insulation: How It Impacts Safety and Performance in Electrical Systems
The insulation of wire cable plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and performance of electrical systems. According to a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), over 30% of electrical failures can be attributed to inadequate insulation, leading to equipment damage and increased maintenance costs. Wire cable insulation not only protects against electrical shock and short circuits but also enhances the longevity and efficiency of the system. With the growing reliance on electrical systems across various sectors, understanding the types of insulation materials and their specific application becomes vital. For instance, materials like PVC and XLPE are commonly used due to their durability and resistance to environmental factors. This "How to" guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into wire cable insulation, emphasizing its significance in minimizing risks and optimizing performance in modern electrical installations.
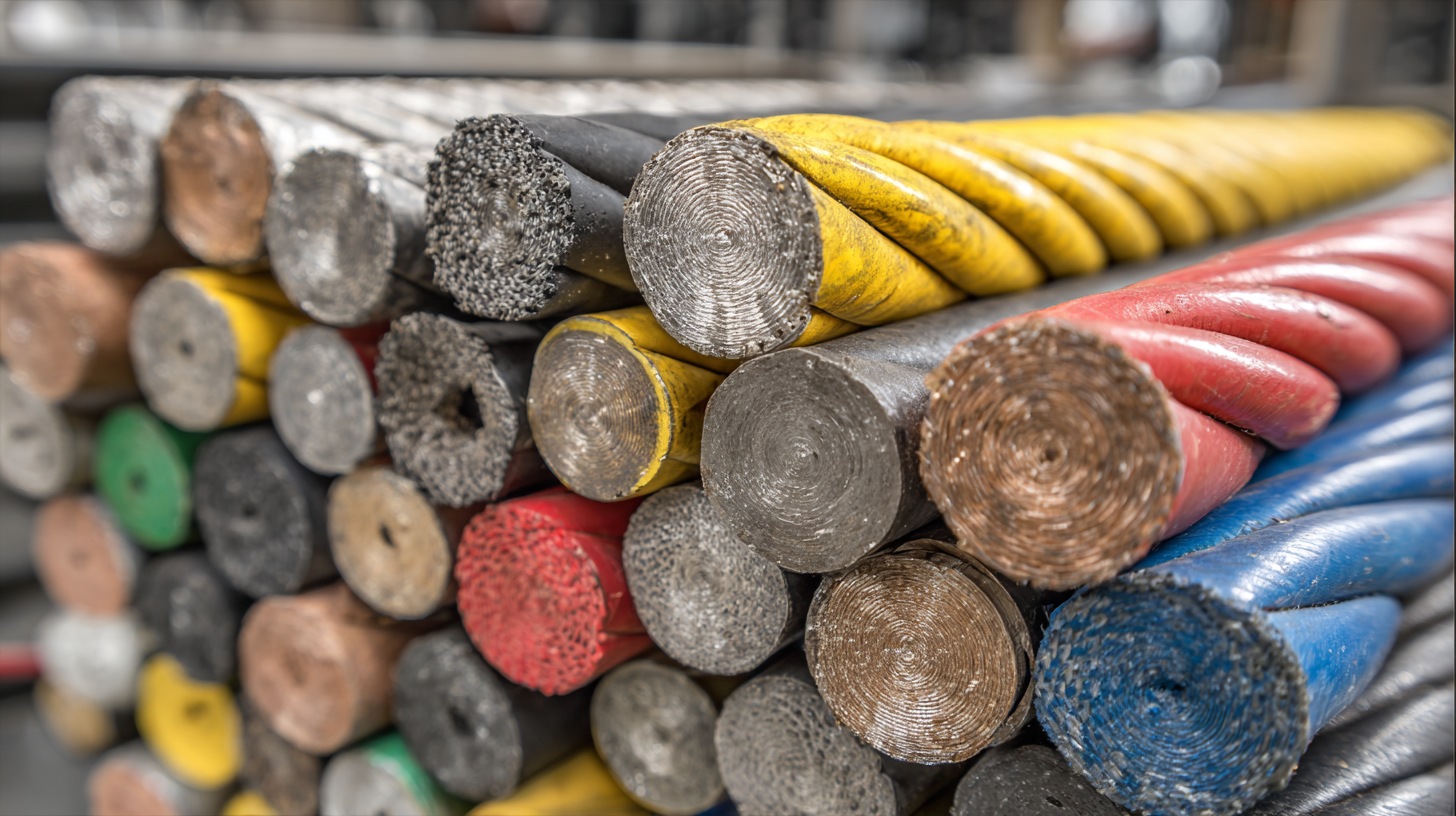

Understanding the Role of Insulation Materials in Electrical Wire Performance
Insulation materials play a critical role in the performance and safety of electrical wires and cables. Specifically, materials such as Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and Polyimide (PI) have been studied for their aging behavior under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and humidity. These materials exhibit varying degrees of resilience and degradation, crucial for applications in aerospace and other demanding environments. Understanding how these insulations respond to thermal oxidative aging can inform better material selection and usage practices, enhancing the overall reliability of electrical systems.
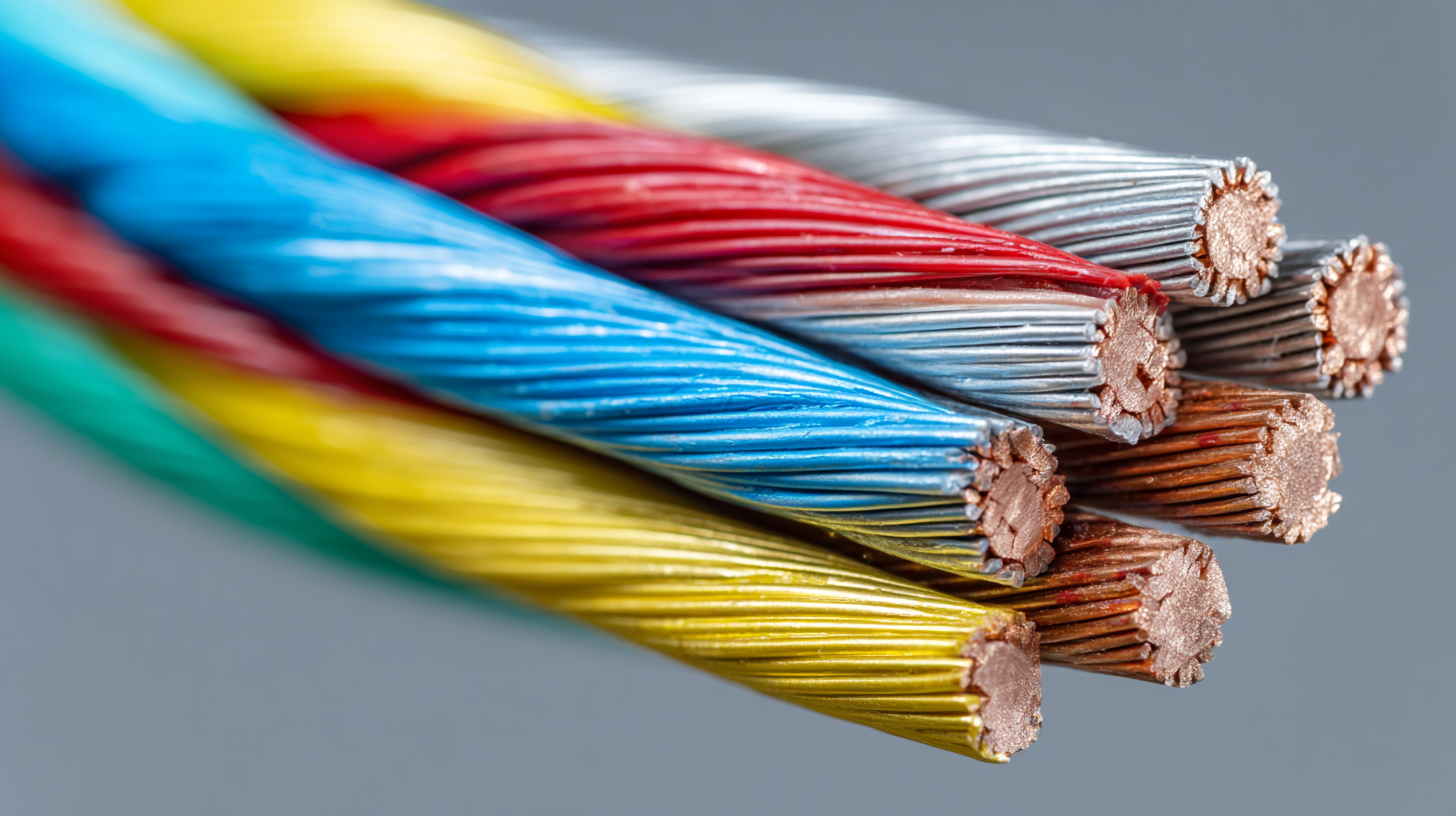
As the demand for sustainable energy sources rises, the market for specialized insulation materials is evolving. The Polyurethane Enamelled Wire market, projected to reach USD 11.68 billion by 2034, illustrates this growth trend driven by the expanded use of electrical systems in renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power. These insulation materials must not only withstand aging and environmental stresses but also contribute to efficient energy transfer, thereby aligning with broader goals of sustainable development and eco-friendly practices in electrical engineering.
Evaluating the Electrical Resistance and Thermal Properties of Insulation Types
Insulation is a critical component of electrical systems, heavily influencing safety and performance. In evaluating insulation types, two main properties—electrical resistance and thermal performance—are paramount. For instance, high-temperature insulation materials like ceramic fibers exhibit excellent thermal resistance due to their composition of aluminum oxide and silica. These materials can maintain structural integrity and function effectively even in extreme environments, making them suitable for advanced electrical applications.
Moreover, the market for transformer insulation papers is projected to grow significantly, with estimates indicating an increase from $120 million in 2022 to $180 million by 2030. This growth underlines the increasing reliance on effective thermal properties in insulating materials to ensure stability and safety in electrical systems. The compound annual growth rate of 5.4% from 2024 to 2030 highlights a robust trend towards improving insulation technology, emphasizing its role in enhancing the overall performance and safety of electrical infrastructures.
Understanding Wire Cable Insulation: How It Impacts Safety and Performance in Electrical Systems
| Insulation Type | Electrical Resistance (Ω·m) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Maximum Operating Temperature (°C) | Flame Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | 1.0 x 10^8 | 0.19 | 70 | Moderate |
| XLPE | 1.0 x 10^15 | 0.35 | 90 | Good |
| Rubber | 1.0 x 10^13 | 0.15 | 80 | Excellent |
| EPR | 1.0 x 10^14 | 0.24 | 90 | Very Good |
Safety Standards in Wire Insulation: National Electrical Code (NEC) Compliance
Wire insulation is a critical aspect of electrical safety and performance, especially as outlined by the National Electrical Code (NEC). Compliance with NEC standards is essential to prevent electrical hazards such as fires, which can be exacerbated by inadequate insulation. Recent incidents, such as the fire at Hyderabad's Gulzar Houz, underscore the dire consequences of insufficient earthing and poor insulation practices. Experts emphasize that addressing these flaws in electrical systems is paramount for ensuring the safety of both structures and their occupants.
The NEC sets forth comprehensive guidelines that must be adhered to when installing wire insulation in various environments, including outdoor settings. These regulations not only promote safe electrical practices but also ensure that systems perform efficiently. For instance, the NEC 690.12 B rule offers critical measures that enhance rapid shutdown capabilities in photovoltaic systems, a requirement that can significantly mitigate risk during emergencies.
Continuous updates, such as the revision of UL 44 for thermoset-insulated wires and cables, reflect the evolving standards designed to bolster safety and operational adequacy in electrical installations across all sectors.
The Impact of Environmental Factors on Wire Insulation Performance and Lifespan
The performance and lifespan of wire cable insulation are significantly influenced by environmental factors. Temperature fluctuations, moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure can all degrade insulation materials over time. High temperatures can cause insulation to become brittle, while excessive moisture can lead to corrosion and failures in electrical conductivity. Understanding these risks is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
Tips for prolonging wire insulation lifespan include selecting materials specifically designed for harsh environments. Use insulation rated for extreme temperatures if the installation area experiences significant heat. Additionally, consider using UV-resistant coatings for outdoor applications to protect against sun damage. Regular inspections should also be conducted to check for any signs of wear or degradation, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement.
Ultimately, being proactive about the environmental factors affecting wire insulation can enhance safety and operational performance. Always keep in mind that the right insulation choice and regular upkeep can make a significant difference in the overall reliability of your electrical systems.
Impact of Environmental Factors on Wire Insulation Performance and Lifespan
Selecting the Right Wire Insulation for Specific Electrical Applications and Conditions
The selection of the right wire insulation is crucial in ensuring the
safety and performance of electrical systems,
particularly in the context of increasing renewable energy applications.
Different insulating materials serve various purposes, from resisting heat and moisture to providing chemical stability.
As the demand for clean energy technologies, such as solar panels and
wind turbines, grows, the need for specialized wire insulation that can
withstand harsh environmental conditions and electrical loads becomes more apparent.
Renewable energy implementations require insulation materials that not only meet
high-performance standards but also adhere to
sustainability principles. For instance, using eco-friendly materials can reduce
the environmental impact of electrical systems while maintaining efficiency.
As industries move toward greener practices, the development of innovative insulation solutions tailored to specific applications will support both
safety standards and performance metrics in diverse electrical environments,
ultimately driving market growth in the renewable sector.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best BNC Cables for Your Home Network
-

Maximizing Your Charge: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Phone Cable for Your Needs
-

Exploring the Future of Coax Cable Innovations at China’s 138th Import and Export Fair 2025
-
Harnessing Fiber Optic Adapter Innovations at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Mastering Cord Management for a Clutter Free Home Environment
-

Exploring the Science Behind RCA Cables: How They Connect Your Audio and Video Devices
